Black gums refer to a condition where the gums appear darker or black in color than their natural pink color. This discoloration can be caused by various factors such as melanin pigmentation, smoking, poor oral hygiene, certain medications, and certain medical conditions. Melanin pigmentation is a common cause of black gums and occurs when the body produces more melanin in the gums. This condition is harmless and is considered to be a normal variant in many people. Smoking is another common cause of black gums. The nicotine and tar in cigarettes can stain the gums and teeth, leading to black or brown discoloration. Poor oral hygiene can also contribute to black gums. When plaque and tartar build-up on the teeth and gums, it can cause the gums to become inflamed and discolored. Certain medications, such as some antimalarial drugs and minocycline, can also cause black gums as a side effect.
Treatment of Black Gums
T he treatment of black gums depends on the underlying cause. Here are some possible treatments for different causes of black gums:
MELANIN PIGMENTATION: This is a harmless condition, and no treatment is necessary. However, if the discoloration is affecting your self-esteem, you can talk to a dentist about options such as cosmetic gum surgery or gum depigmentation.
QUIT SMOKING: Quitting smoking is the best way to prevent further staining of the gums and teeth. Professional teeth cleaning and teeth whitening treatments may help remove the existing stains.
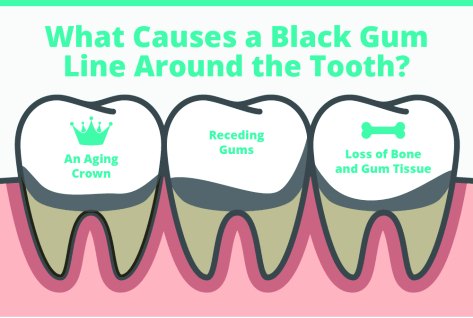
MAINTAINING GOOD ORAL HYGIENE PRACTICES: Brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash can help prevent gum discoloration due to poor oral hygiene.
If a medication is causing black gums, your healthcare provider may recommend a change in medication or a lower dosage.
If black gums are caused by a medical condition, such as Addison’s disease or Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, treatment will focus on addressing the underlying condition.